full body check millimeter wave scanner
Full Body Millimeter-Wave Security Scanner
1. Introduction
Importance of modern security screening
Rising global demand for efficient and precise people inspection
Transition from traditional methods (metal detectors, pat-downs) to advanced millimeter-wave scanning
2. Precise Security Screening
Detection of concealed weapons, explosives, contraband
Screening of high-risk/key individuals
Role in anti-terrorism, aviation, and public events
High accuracy & reliability
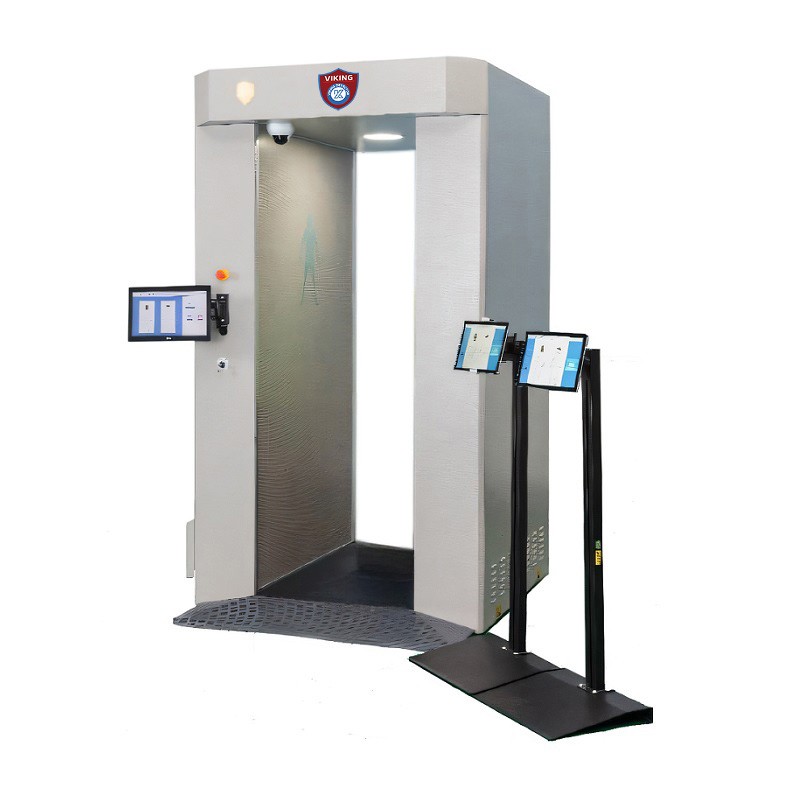
3. People Flow Management & Integration with X-Ray Machines
Flow coordination between body scanners and baggage X-ray scanners
Systematic management of passenger movement
Efficiency in airports, subways, stadiums
4. Throughput of Security Channels
Range: 100–600 people/hour
Single inspection time: less than 3 seconds
Comparison with other methods
Adaptability for peak traffic in large venues
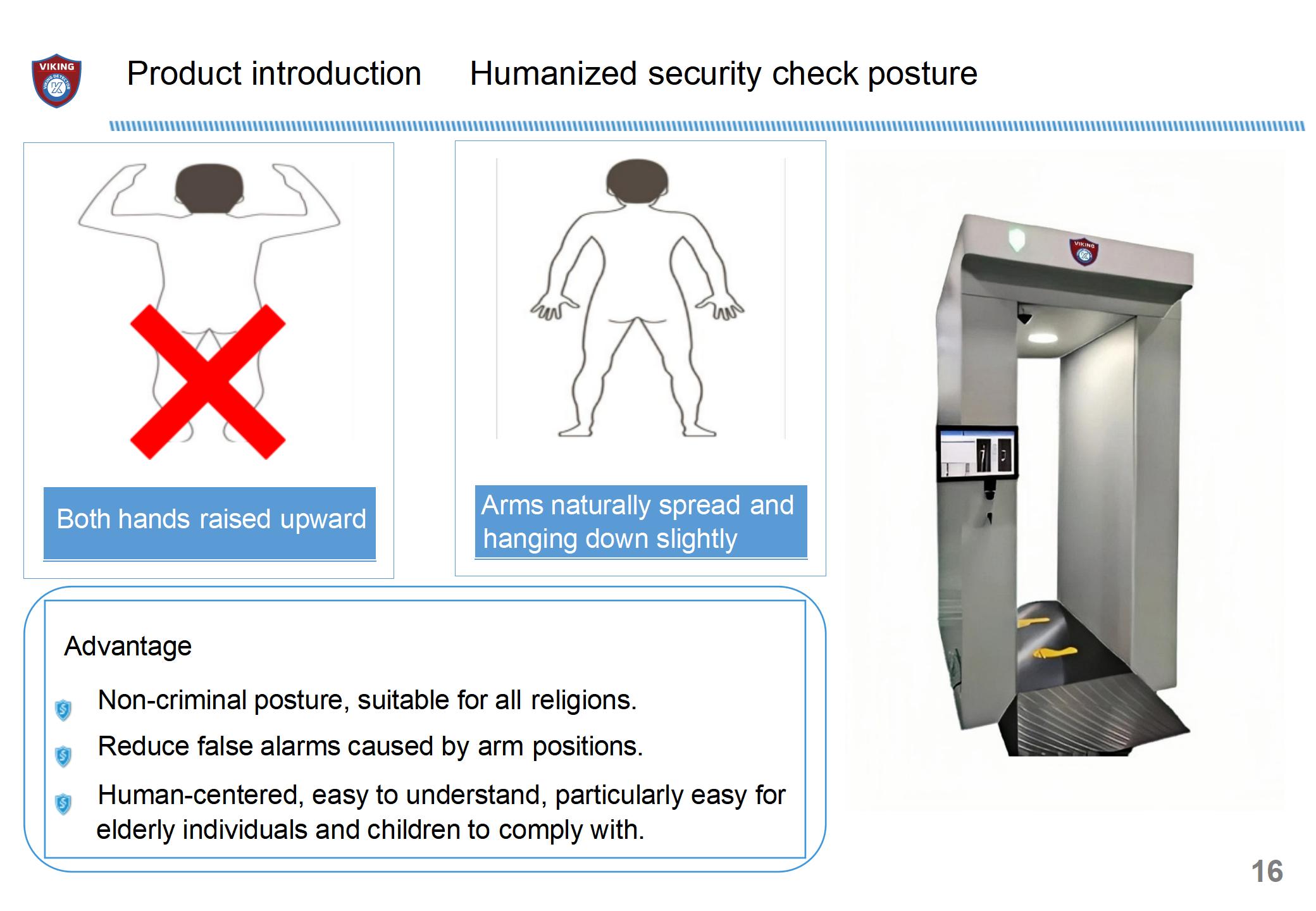
5. Cooperation from Screened Individuals
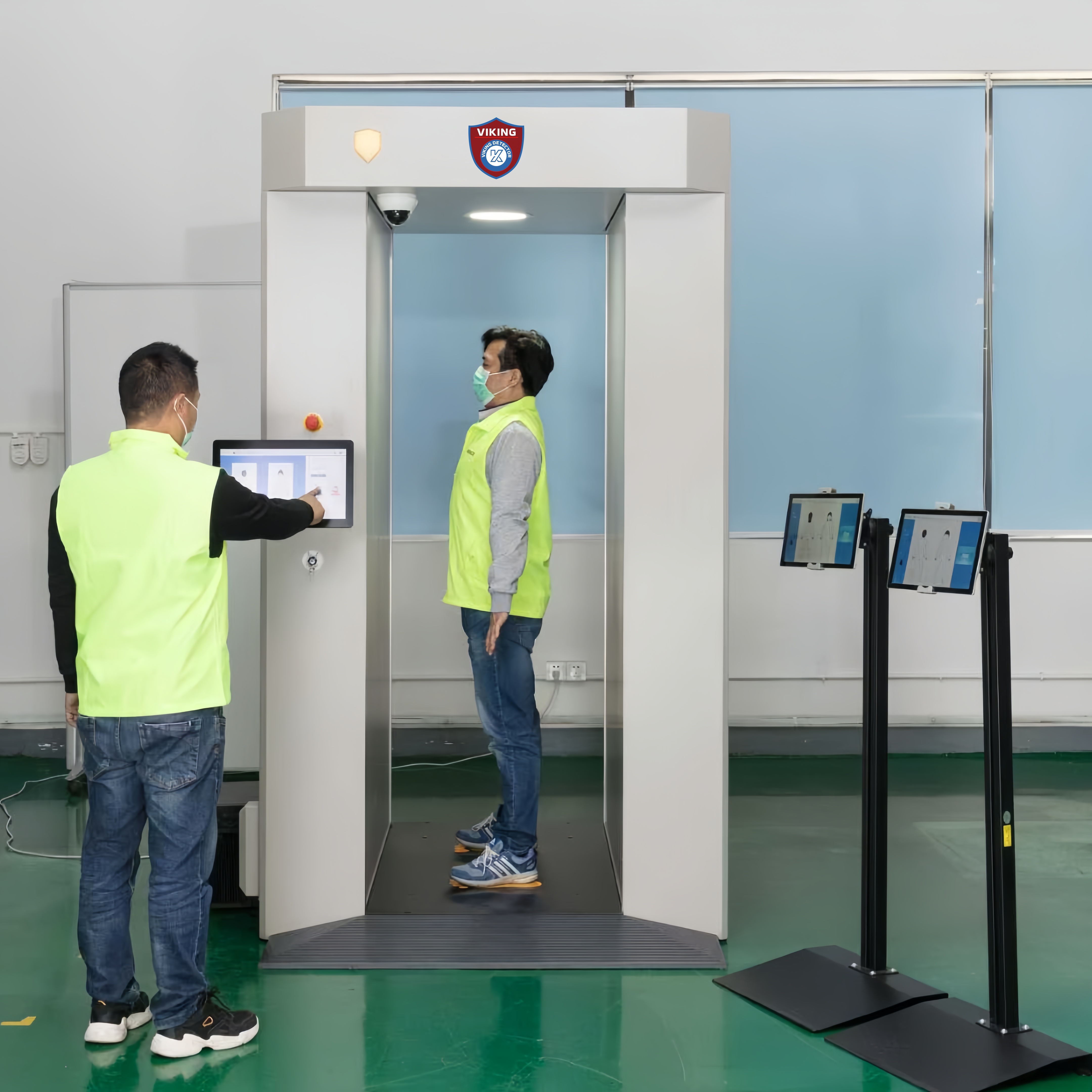
Non-contact and non-invasive scanning
Attire & posture requirements (arms naturally down)
How behavior affects scanning efficiency
Training & awareness for smoother operation
6. International Standards and Applications
Europe & US: Over 15 years of standardized use
Mature technologies, privacy protection, and safety standards
China: Official standards released in 2018
Compliance with aviation security and customs regulations
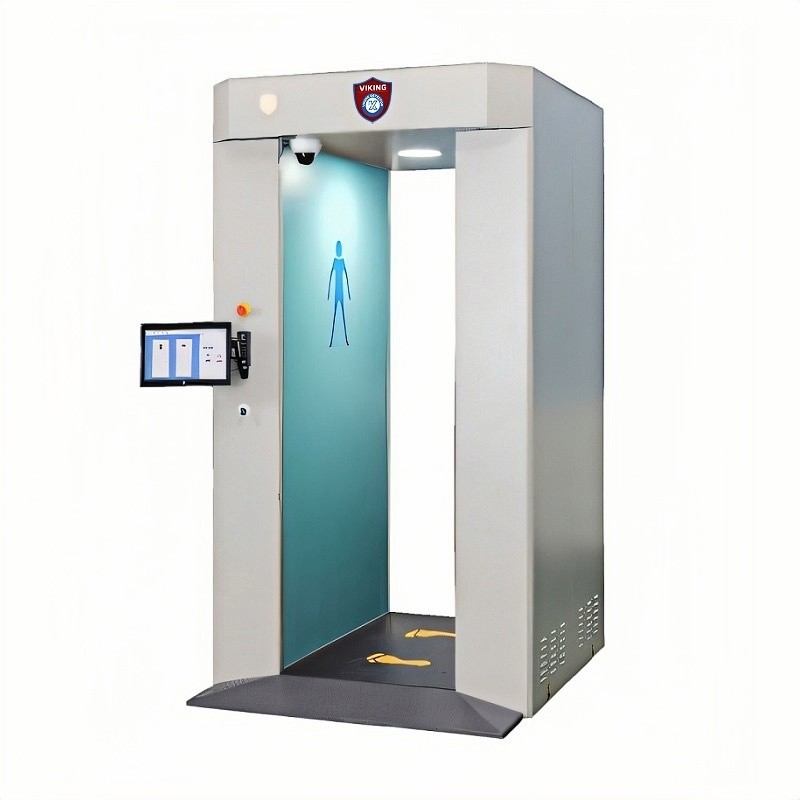
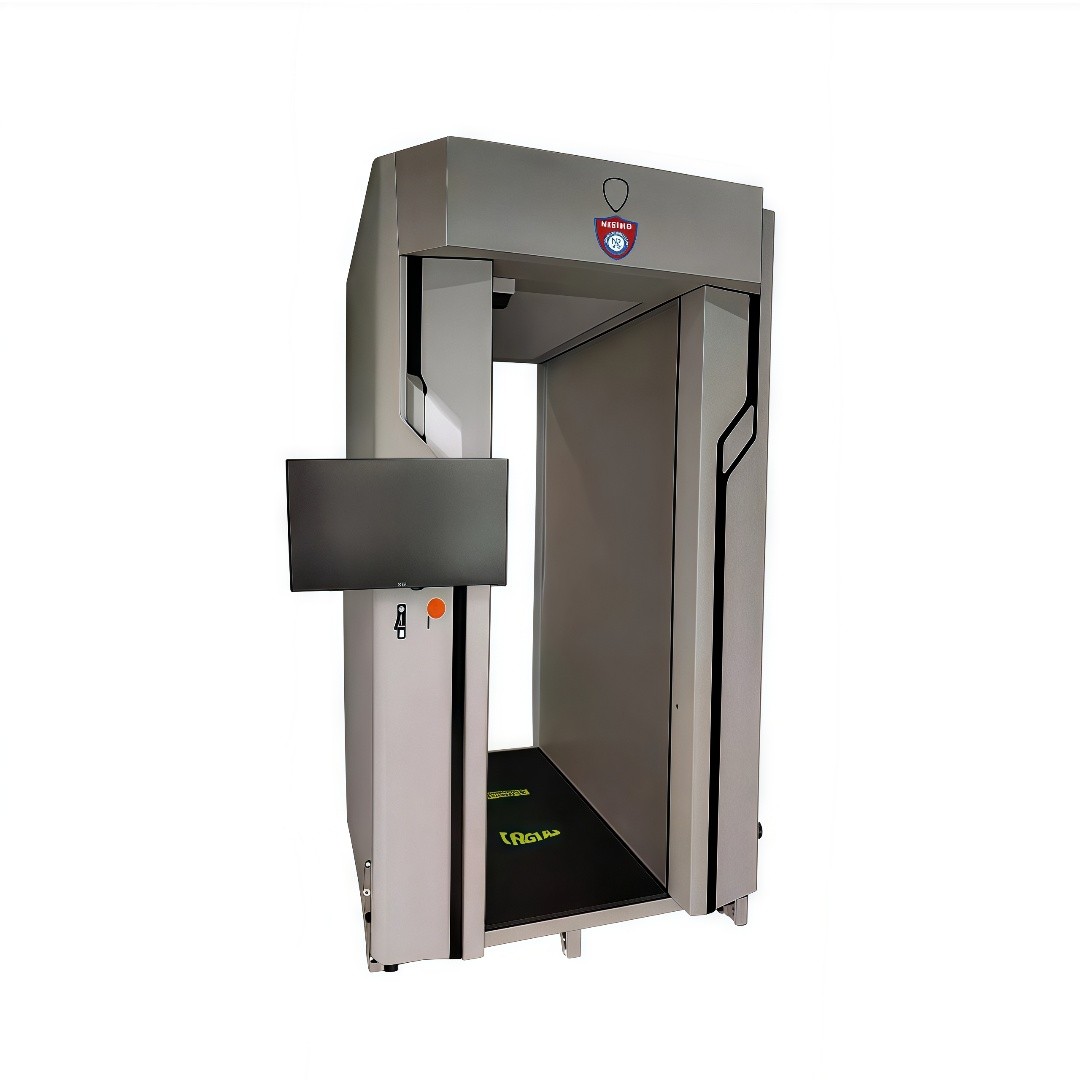
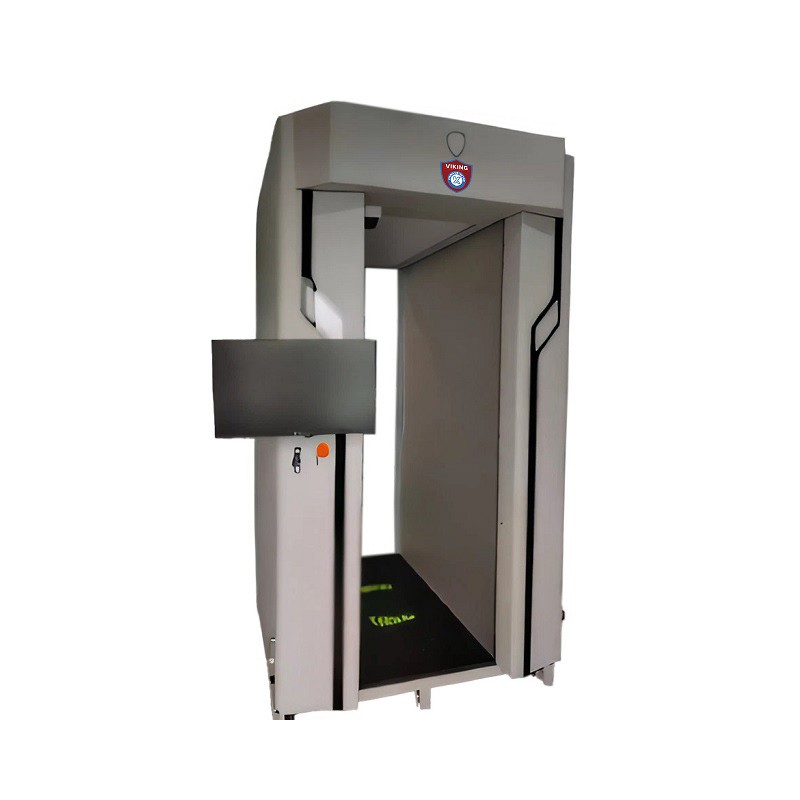
7. Technical Features & Specifications
Imaging Principle: Active millimeter-wave imaging
Scanning Method: Planar array vertical scanning
Mode: Non-contact, non-ionizing radiation
Scan Area: Height 0.1–2m, Width 1.2m
Resolution: Line ≤2mm, Spatial ≤5mm
Single Detection Time: 3 seconds
Throughput: Up to 600 people/hour
Alarm System: Automatic red-box highlight of threats
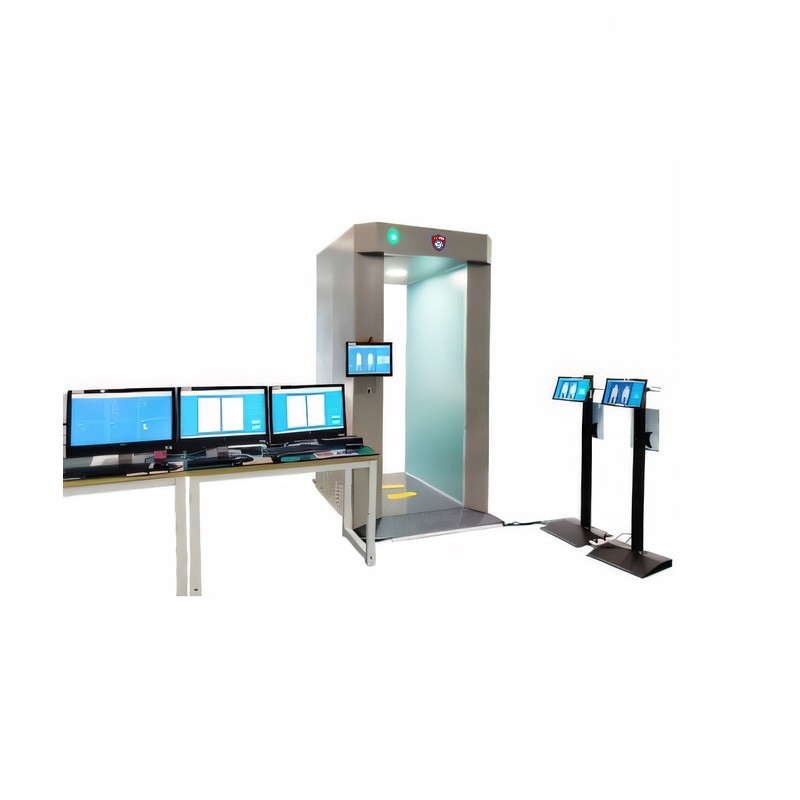
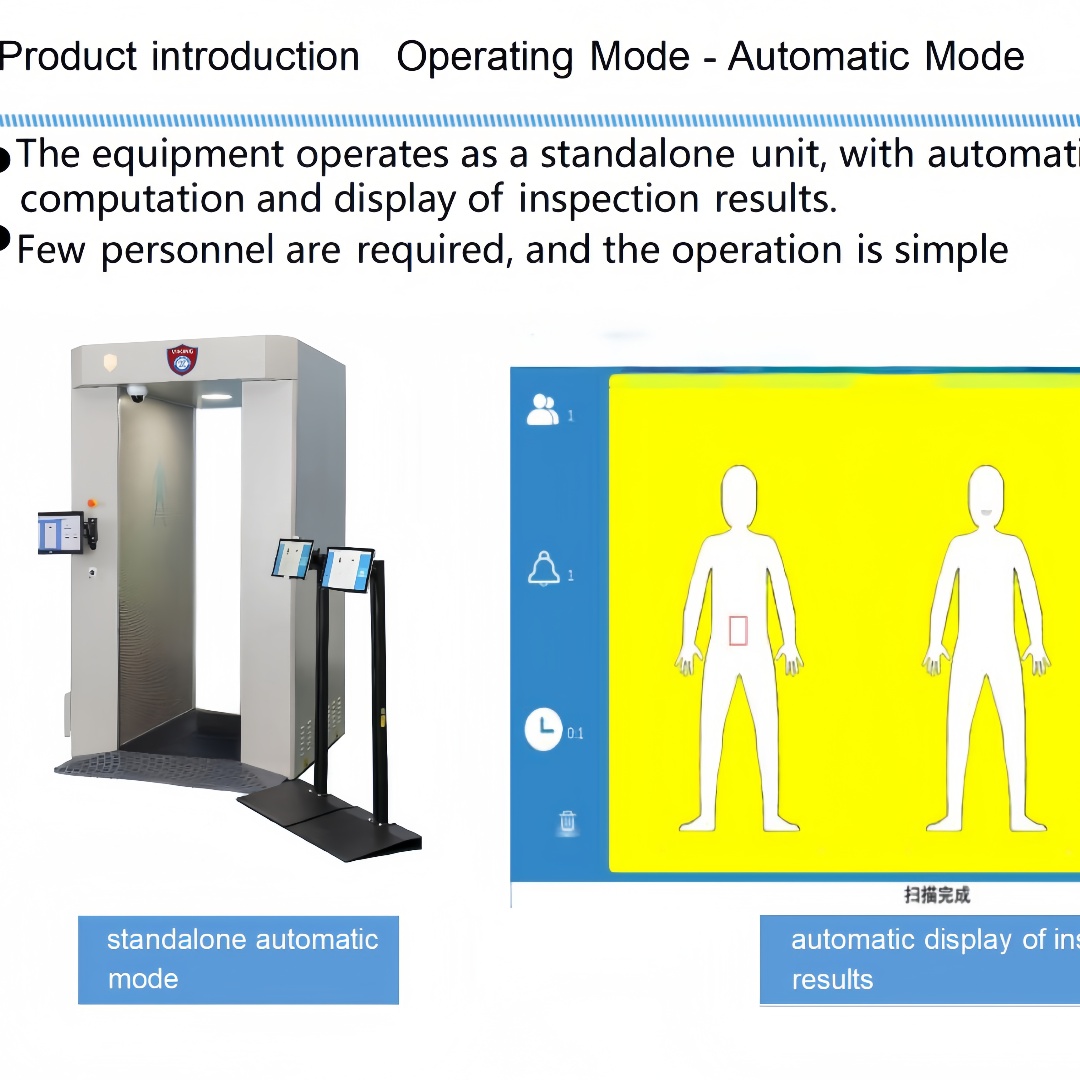
Working Modes: Automatic / Remote analysis / Multi-machine interconnection
Core Functions: Image processing, user management, system log
Dimensions: 2400 × 1300 × 1300 mm
Weight: <500kg
Passage Size: 2100 × 800 mm
8. Ease of Operation & Installation
One-click operation
Modular design for easy installation
Quick learning curve for security staff
9. Safety and Reliability
Non-ionizing radiation ensures safety
High reliability with continuous operation
Proven track record in international use
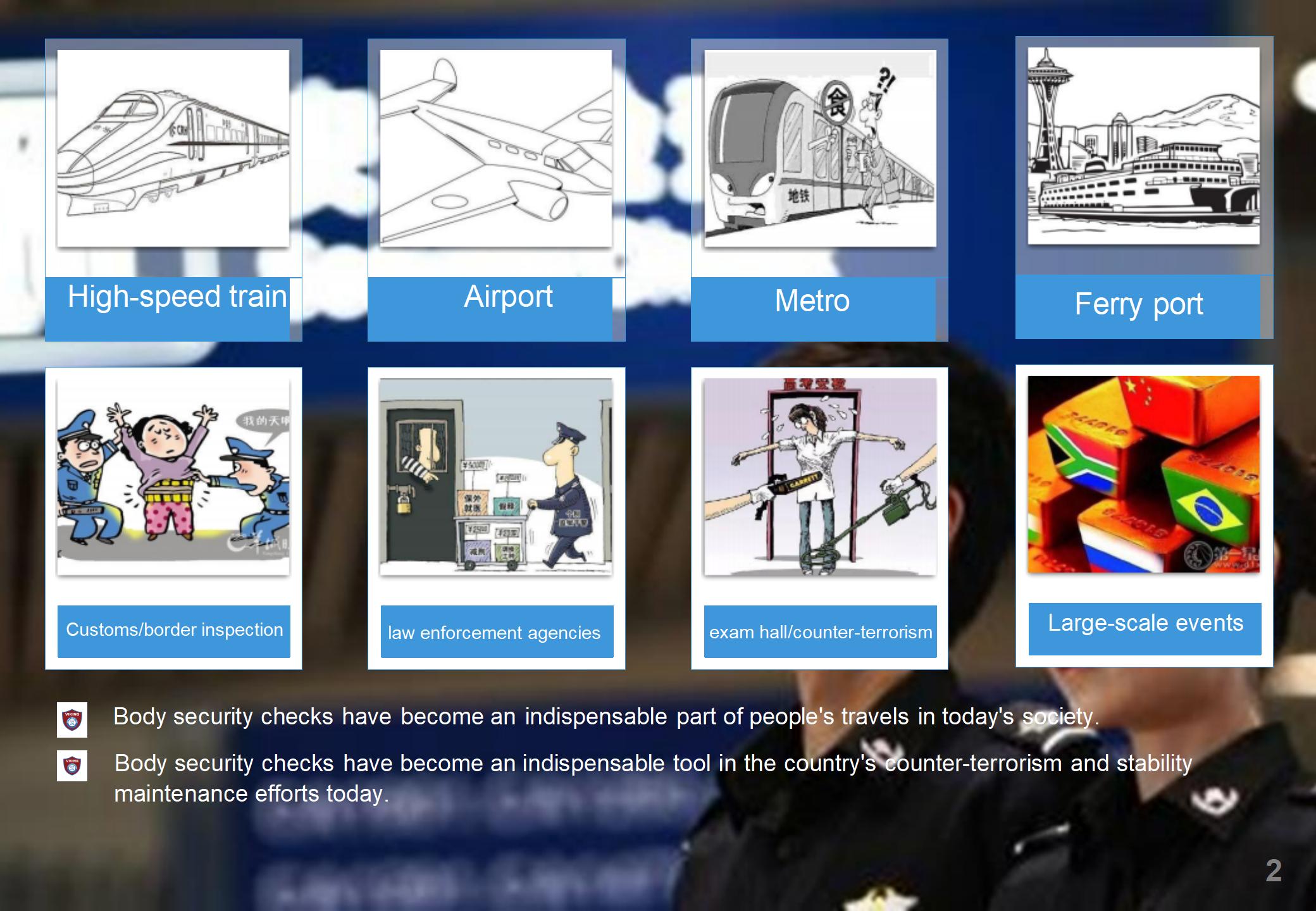
10. Applications
Airports: Primary use in passenger security screening
Subways & Railways: Preventing dangerous goods
Customs & Border Security: Smuggling prevention
Events & Stadiums: Managing large crowds safely
Government & High-Security Facilities
11. Advantages over Traditional Screening
Faster than pat-downs
More accurate than handheld detectors
Better passenger experience (non-invasive)
12. Conclusion
Reinforcement of importance in modern security infrastructure
Long-term cost-effectiveness
Call to action for deployment in high-traffic security hubs
technical principles | active millimeter-wave imaging |
scanning method | planar array vertical scanning |
inspection mode | Non-contact, non-ionizing radiation; the person being inspected completes the scanning imaging with the arms naturally hanging down |
scan area | Height: 0.1m-2m, Width: 1.2m |
image accuracy | Line Resolution: ≤2mm, Spatial Resolution: ≤5mm |
single detection time | 3 seconds,i.e., throughput [100, 600] people per hour |
automatic alarm | The system is capable of inspecting various types of firearms, explosives or combustible materials and devices, controlled items, hazardous substances, and other objects. It issues an alarm notification by outlining concealed items with red boxes, indicating their size and location |
working mode | It has automatic mode and remote image analysis mode, and can be interconnected with multiple machines |
core functionality | It has various image processing, user, log, and system management functions |
external dimensions | 2400mm (H) ×1300mm (W) ×1300mm (D) |
weight | <500Kg |
passage dimensions | 2100mm (H) ×800mm (W) |









